How To Improve WordPress Performance By Configuring W3TC

Every now and then in the WordPress ecosystem you might see people asking or talking about speeding up a WordPress website. Speed-related topics are one of the most talked about in the industry, but I would say most people know very little about it.
Improve WordPress Performance using W3TC
Why Is Speed Necessary for Your WordPress Website?
Well, a website that loads under 2 seconds or less will deliver a better user experience to your visitors and you will have a better chance of ranking higher in the SERPs (search engine ranking pages)
There are over 26+ ways to speed up your WordPress website, but the best among them is to use a WordPress caching plugin, like W3TC.
W3 Total Cache (W3TC) is one of the best free WordPress caching plugins available. It contains a lot of customization options. and along with that, you get to learn a lot about various types of caches that can be used to improve a WordPress site’s performance.
Understanding W3TC can be difficult for some of us. Therefore, in this tutorial, I will do my best to quickly give you an overview of the settings you should use and in which scenario it will be best to consider a certain setting over the other.
W3TC Settings Explained
At first, you might feel intimidated with the number of settings that W3 Total Cache has. If you are new to W3 Total Cache, then I would suggest you look into the “General Settings” tab first.
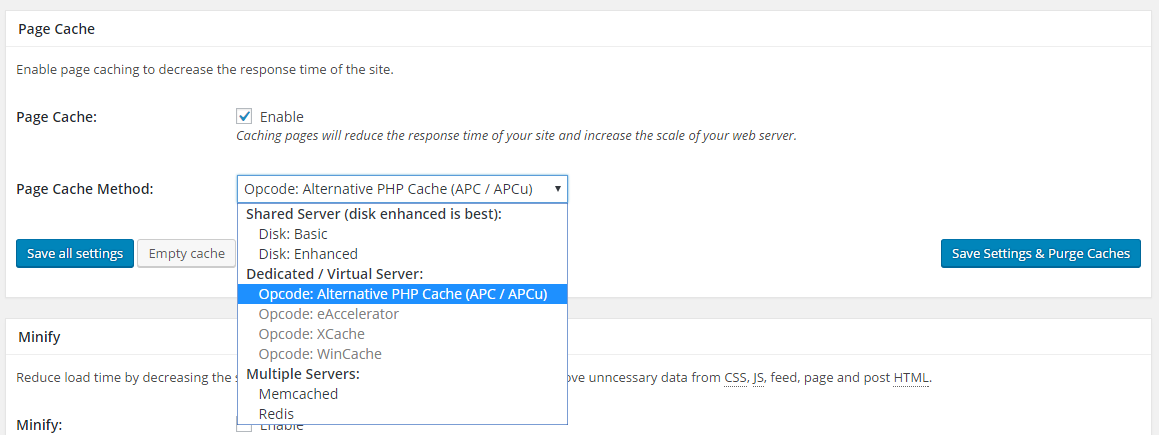
1. Page Cache
The Page Cache option in the W3TC enables the caching of your WordPress website’s frontend pages. The page cache builds your WordPress pages and posts into static HTML files. These cached HTML versions can be served to a browser much quickly, thus saving a lot of execution time and resources of your server.
Recommended settings of Page Cache will vary based on the hosting environment you are using.
If you are hosting using a shared server, then the best setting would be Disk Enhanced. This will utilize the hard drive or SSD of your server to store the cached HTML static files.
If you are on a VPS or a dedicated server with OpCode installed, then you should use a better option like APC.
You should always be using Page Cache on all of your WordPress websites.
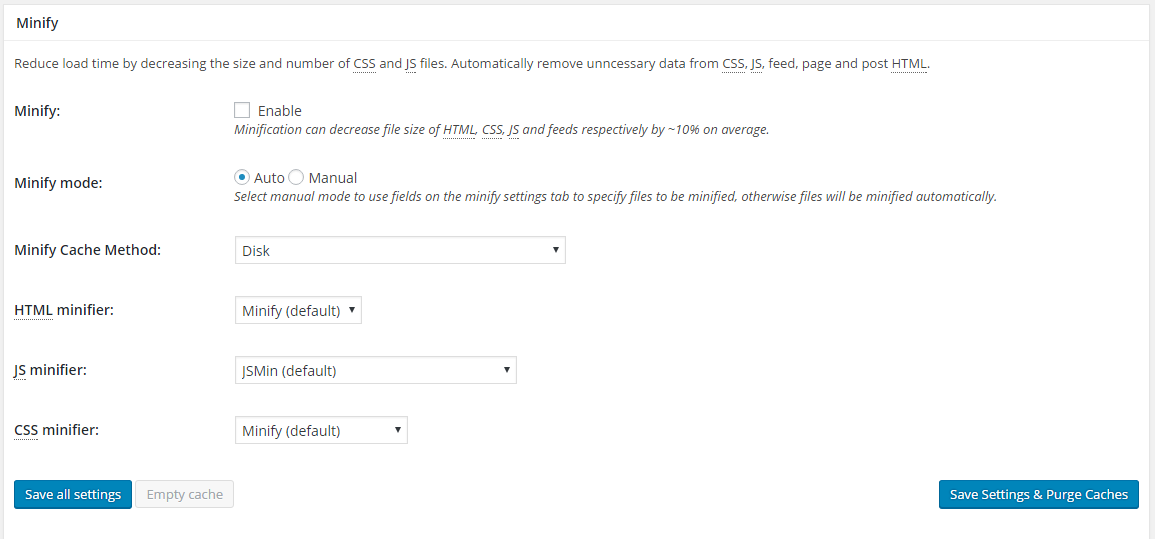
2. Minify
Minifying CSS, JS, and HTML of your website have been considered one of the most widely used techniques to make it lightweight.
Minifying through a plugin is not considered the best option when it comes to WordPress, as it can have a negative impact on the performance of WordPress if you are hosting on a low-end server or a shared server.
Recommended Minify Settings
For shared server: Keep it Disabled
For dedicated, VPS, or cloud server: Enable it
Minify Mode: Auto
HTML Minifier: Minify (Default)
JS Minifier: YUI Compressor
CSS Minifier: YUI Compressor
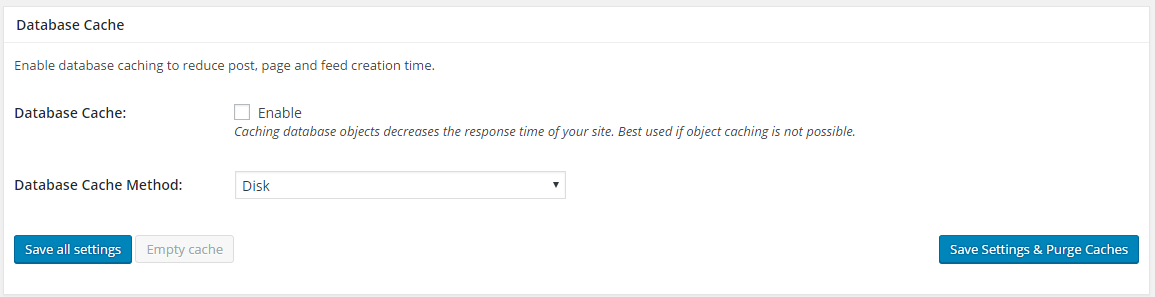
3. Database Cache
Whenever a WordPress page renders, it sends a lot of requests to its database. The amount of database requests increases when you start adding elements like image, video, and audio files.
Each query has its own response time and each request adds to the response time of your WordPress website that greatly increases its loading time.
Database cache can reduce the number of database queries by temporarily storing them, either in the disk of the server or in the Opcode cache.
Recommended Database Cache Settings
For shared server: Keep it Enabled
Database Cache Method: Disk
For dedicated, VPS, or cloud server: Enable
Object Cache Method: APC or Memcached
Redis and Memcached are better performing database caches and some hosting providers have it pre-installed on their servers. Ask your hosting provider if they have (or can) install Redis or Memcached on your servers.
Other than using a Database Cache, you can also speed up database performance by optimizing the WordPress database manually or through code.
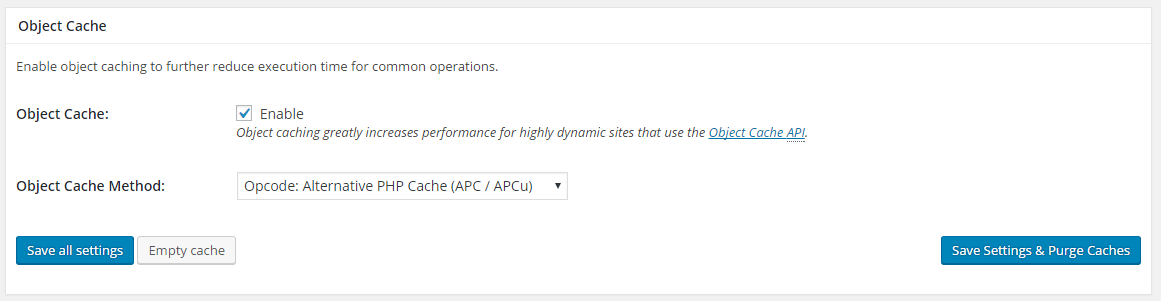
4. Object Cache
Object is a collection of data that is grouped together. Objects can be cached and served much efficiently without accessing the origin source. Object cache is considered one of the most efficient and powerful caches that can be used on a WordPress website.
To understand more about WP Object Cache, read this codex entry on WordPress.org.
Recommended Object Cache Settings
For shared server: Keep it Enabled
Object Cache Method: Disk or APC
For dedicated, VPS, or cloud server: Enable
Object Cache Method: Redis or Memcached
Again I will mention that, you need to be sure that Redis or Memcached is installed on your web hosting server.
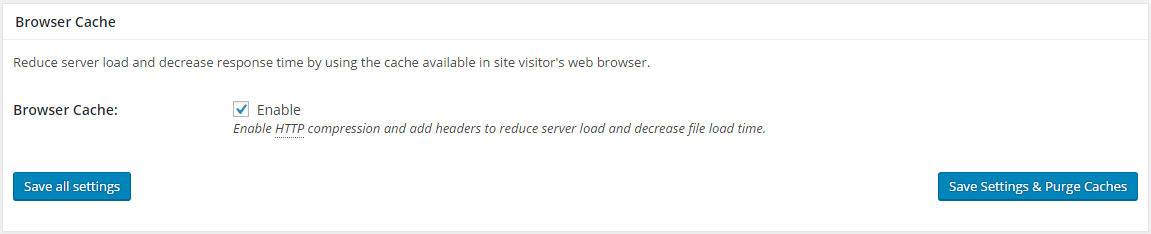
5. Browser Cache
Browsers available these days cache files of the websites you mostly visit on the local disks of the devices. This reduces website loading time when a visitor is revisiting a website as most of the assets are loaded from the device’s disk.
Keeping browser cache enabled is recommended for every kind of WordPress website no matter what. These settings tell the browser that they are allowed to cache the files.
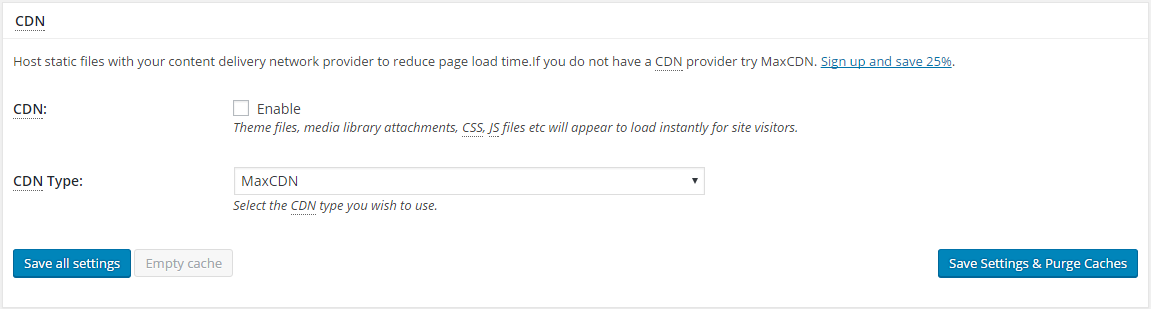
6. CDN
This setting lets you configure a content delivery network on your WordPress website. Content delivery networks are distributed servers that keep a copy of your WordPress files like images, CSS, JS, and HTML files.
The CDN will serve most of the static files to your visitors. This will cut the load of your web server to improve the overall performance of your WordPress website.
You will need to purchase a CDN account and configure it on your WordPress website. If you are confused about which CDN to use, then you can refer to the CDN options available in the W3TC drop-down menu.
Amazon Cloudfront and MaxCDN are widely popular in the WordPress community.
Check out the best CDN providers of 2018
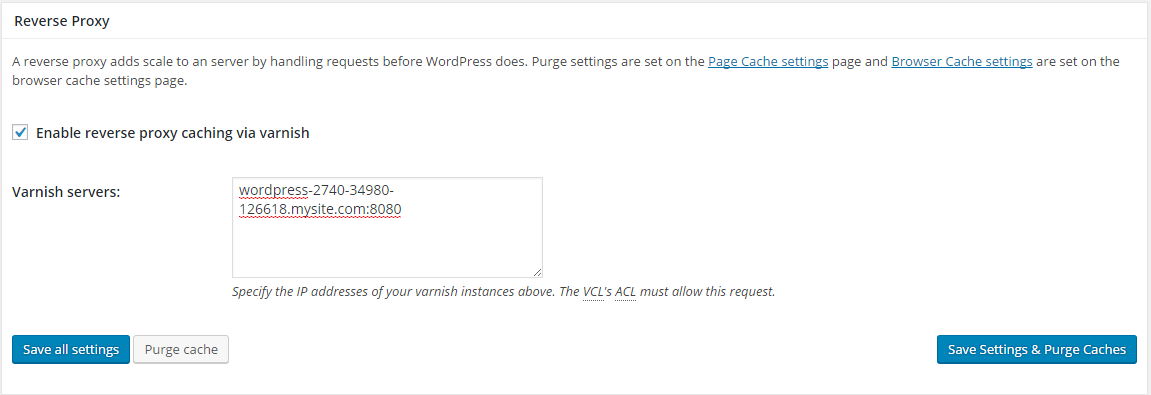
7. Reverse Proxy
Putting WordPress behind a reverse proxy like Varnish will improve the performance by not letting WordPress handle any requests.
Varnish cache’s official site claims that it speeds up websites by 300 to 1000 times. What it does is cache all the contents of a website and serves the HTTP requests. Technically it eliminates the load of your server.
If you have Varnish cache installed on your server or your hosting provider has it pre-configured, then you should definitely be using it on your live websites.
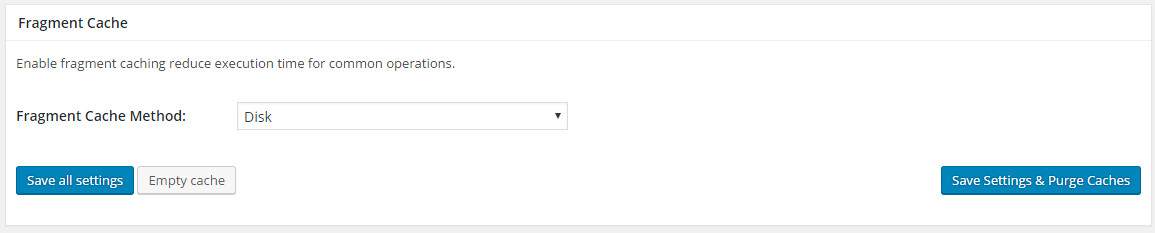
8. Fragment Cache
Dynamic PHP functions make up WordPress themes and plugins. Each code is executed and queried multiple times by WordPress.
Caching a dynamic block of PHP code is called Fragment Caching. This cache will store the common operations that occur in your themes and plugins.
Configuring this is no easy task if you are not a developer or the one who doesn’t have an understanding about WordPress themes or plugins.
To use Fragment Cache in W3TC, you will need to register fragment groups. To define fragment groups, you will need to enable support of W3TC fragment cache by adding the following code in wp-config.php file.
|
1 |
define('W3TC_DYNAMIC_SECURITY', 'somesecurestring'); |
To apply fragment caching on any PHP code, enclose it like the example shown below.
|
1 |
<!-- mfunc W3TC_DYNAMIC_SECURITY -->any PHP code<!-- /mfunc W3TC_DYNAMIC_SECURITY > |
You can refer to W3TC FAQs to know more about fragment caching.
Debugging W3TC
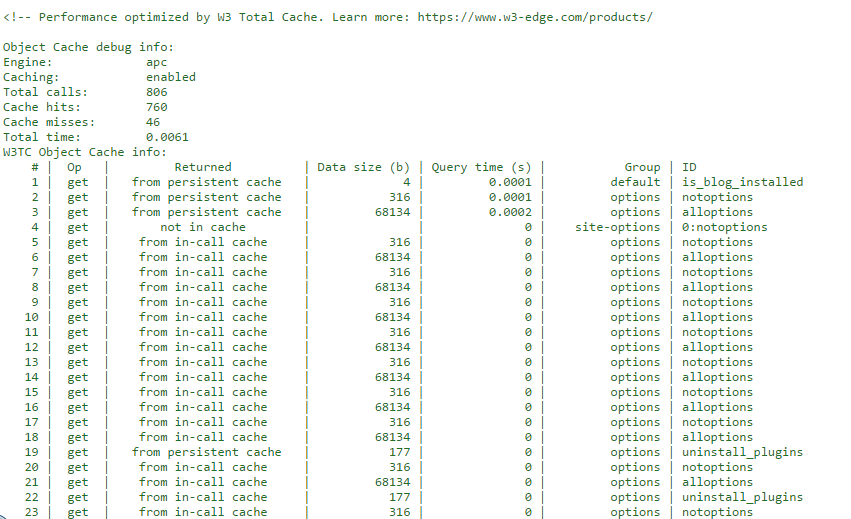
If you are curious to know more about the impact and the results of the W3 Total Cache, then you can enable Debug and see a log of caches that you are using in the source code of your website, as shown in the image below.
Conclusion
I have covered the general settings you need to have in place on your WordPress website to make it perform better. W3TC is undoubtedly one of the most powerful WordPress caching plugins available today.
This plugin gives you the freedom to configure and customize the caches. What I appreciate about this plugin is that while using it, you get to learn a lot about the different caches and what role they play.
The configuration of W3TC largely depends on your hosting environment. So make sure you have the best configurations in place.

Create Faster WordPress Websites!
Free eBook on WordPress Performance right in your inbox.